Grid5000:Home: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (74 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{|width="95%" | {|width="95%" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|bgcolor="# | |bgcolor="#888888" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:2em;padding-top:1em;"| | ||
[[ | [[File:Slices-ri-white-color.png|260px|left|link=https://www.slices-ri.eu]] | ||
< | <b>Grid'5000 is a precursor infrastructure of [https://www.slices-ri.eu SLICES-RI], Scientific Large Scale Infrastructure for Computing/Communication Experimental Studies.</b> | ||
<br/> | |||
Content on this website is partly outdated. Technical information remains relevant. | |||
|} | |} | ||
{|width="95%" | |||
|- valign="top" | |||
|bgcolor="#f5fff5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | |||
[[Image:g5k-backbone.png|thumbnail|260px|right|Grid'5000|link=https://www.grid5000.fr]] | |||
'''Grid'5000 is a large-scale and flexible testbed for experiment-driven research in all areas of computer science, with a focus on parallel and distributed computing, including Cloud, HPC, Big Data and AI.''' | |||
Key features: | |||
* provides '''access to a large amount of resources''': 15000 cores, 800 compute-nodes grouped in homogeneous clusters, and featuring various technologies: PMEM, GPU, SSD, NVMe, 10G and 25G Ethernet, Infiniband, Omni-Path | |||
* '''highly reconfigurable and controllable''': researchers can experiment with a fully customized software stack thanks to bare-metal deployment features, and can isolate their experiment at the networking layer | |||
* '''advanced monitoring and measurement features for traces collection of networking and power consumption''', providing a deep understanding of experiments | |||
* '''designed to support Open Science and reproducible research''', with full traceability of infrastructure and software changes on the testbed | |||
* '''a vibrant community''' of 500+ users supported by a solid technical team | |||
<br> | |||
Read more about our [[Team|teams]], our [[Publications|publications]], and the [[Grid5000:UsagePolicy|usage policy]] of the testbed. Then [[Grid5000:Get_an_account|get an account]], and learn how to use the testbed with our [[Getting_Started|Getting Started tutorial]] and the rest of our [[:Category:Portal:User|Users portal]]. | |||
<br> | |||
Published documents and presentations: | |||
* [[Media:Grid5000.pdf|Presentation of Grid'5000]] (April 2019) | |||
* [https://www.grid5000.fr/mediawiki/images/Grid5000_science-advisory-board_report_2018.pdf Report from the Grid'5000 Science Advisory Board (2018)] | |||
Older documents: | |||
* [https://www.grid5000.fr/slides/2014-09-24-Cluster2014-KeynoteFD-v2.pdf Slides from Frederic Desprez's keynote at IEEE CLUSTER 2014] | |||
* | * [https://www.grid5000.fr/ScientificCommittee/SAB%20report%20final%20short.pdf Report from the Grid'5000 Science Advisory Board (2014)] | ||
<br> | |||
Grid'5000 is supported by a scientific interest group (GIS) hosted by Inria and including CNRS, RENATER and several Universities as well as other organizations. Inria has been supporting Grid'5000 through ADT ALADDIN-G5K (2007-2013), ADT LAPLACE (2014-2016), and IPL [[Hemera|HEMERA]] (2010-2014). | |||
|} | |||
[[ | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
{{#status:0|0|0|http://bugzilla.grid5000.fr/status/upcoming.json}} | |||
<br> | |||
== Random pick of publications == | |||
{{#publications:}} | |||
==Latest news== | |||
<rss max=4 item-max-length="2000">https://www.grid5000.fr/rss/G5KNews.php</rss> | |||
---- | |||
[[News|Read more news]] | |||
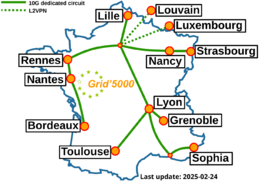
=== | === Grid'5000 sites=== | ||
{|width=" | {|width="100%" cellspacing="3" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
|width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | |width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
* [[Grenoble:Home|Grenoble]] | * [[Grenoble:Home|Grenoble]] | ||
* [[Lille:Home|Lille]] | * [[Lille:Home|Lille]] | ||
* [[Luxembourg:Home|Luxembourg]] | * [[Luxembourg:Home|Luxembourg]] | ||
* [[Louvain:Home|Louvain]] | |||
|width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | |width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
* [[Lyon:Home|Lyon]] | * [[Lyon:Home|Lyon]] | ||
* [[Nancy:Home|Nancy]] | * [[Nancy:Home|Nancy]] | ||
* [[Nantes:Home|Nantes]] | * [[Nantes:Home|Nantes]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Rennes:Home|Rennes]] | ||
|width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | |width="33%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
* [[Sophia:Home|Sophia-Antipolis]] | * [[Sophia:Home|Sophia-Antipolis]] | ||
* [[Strasbourg:Home|Strasbourg]] | |||
* [[Toulouse:Home|Toulouse]] | * [[Toulouse:Home|Toulouse]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Current funding == | == Current funding == | ||
{|width="100%" cellspacing="3" | {|width="100%" cellspacing="3" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | | width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
===INRIA=== | ===INRIA=== | ||
[[Image:Logo_INRIA.gif|300px]] | [[Image:Logo_INRIA.gif|300px|link=https://www.inria.fr]] | ||
| width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | | width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
===CNRS=== | ===CNRS=== | ||
[[Image:CNRS-filaire- | [[Image:CNRS-filaire-Quadri.png|125px|link=https://www.cnrs.fr]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | | width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
===Universities=== | ===Universities=== | ||
IMT Atlantique<br/> | |||
Université Grenoble Alpes, Grenoble INP<br/> | |||
Université Rennes 1, Rennes<br/> | |||
Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse / INSA / FERIA / Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse<br/> | Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse / INSA / FERIA / Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse<br/> | ||
Université Bordeaux 1, Bordeaux<br/> | |||
Université Lille 1, Lille<br/> | |||
École Normale Supérieure, Lyon<br/> | |||
| width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | | width="50%" bgcolor="#f5f5f5" valign="top" align="center" style="border:1px solid #cccccc;padding:1em;padding-top:0.5em;"| | ||
===Regional councils=== | ===Regional councils=== | ||
Aquitaine<br/> | Aquitaine<br/> | ||
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes<br/> | |||
Bretagne<br/> | Bretagne<br/> | ||
Champagne-Ardenne<br/> | Champagne-Ardenne<br/> | ||
Provence Alpes Côte d'Azur<br/> | Provence Alpes Côte d'Azur<br/> | ||
Hauts de France<br/> | |||
Lorraine<br/> | Lorraine<br/> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:02, 11 July 2025
|
Grid'5000 is a precursor infrastructure of SLICES-RI, Scientific Large Scale Infrastructure for Computing/Communication Experimental Studies.
|
|
Grid'5000 is a large-scale and flexible testbed for experiment-driven research in all areas of computer science, with a focus on parallel and distributed computing, including Cloud, HPC, Big Data and AI. Key features:
Older documents:
|
Random pick of publications
Five random publications that benefited from Grid'5000 (at least 2780 overall):
- Elana Courtines, Georges da Costa, Patricia Stolf. CuttleBench: A benchmarking tool for comparing programming languages' performances. Toulouse 3 Paul Sabatier. 2023. hal-04610856 view on HAL pdf
- Xiao Peng, Olivier Simonin, Christine Solnon. Non-Crossing Anonymous MAPF for Tethered Robots. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2023, 78, pp.357-384. 10.1613/jair.1.14351. hal-04216937 view on HAL pdf
- Quentin Guilloteau, Sophie Cerf, Raphaël Bleuse, Bogdan Robu, Eric Rutten. Under Control: A Control Theory Introduction for Computer Scientists. ACSOS 2024 - 5th IEEE International Conference on Autonomic Computing and Self-Organizing Systems (ACSOS 2024), Sep 2024, Aahrus, Denmark. pp.1-10. hal-04666859 view on HAL pdf
- Thomas Firmin, Pierre Boulet, El-Ghazali Talbi. Asynchronous Multi-fidelity Hyperparameter Optimization Of Spiking Neural Networks. International Conference on Neuromorphic Systems (ICONS 2024), Jul 2024, Washington, United States. hal-04781629 view on HAL pdf
- Pierre-François Gimenez, Jérôme Mengin. Learning Conditional Preference Networks: an Approach Based on the Minimum Description Length Principle. IJCAI 2024 - 33rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Aug 2024, Jeju, South Korea. pp.3395-3403, 10.24963/ijcai.2024/376. hal-04572196 view on HAL pdf
Latest news
The first SLICES-FR School is organized from July 7th to 11th in Lyon.
This free event, co-organized with the PEPR Cloud and Networks of the Future, brings together researchers, engineers and professionals to explore advances in distributed computing, edge computing, reprogrammable networks and the IoT.
![]() Cluster "vianden" is now in the default queue in Luxembourg
Cluster "vianden" is now in the default queue in Luxembourg
We are pleased to announce that the vianden[1] cluster of Luxembourg is now available in the default queue.
Vianden is a cluster of a single node with 8 MI300X AMD GPUs.
The node features:
The AMD MI300X GPUs are not supported by Grid'5000 default system (Debian 11). However, one can easily unlock full GPU functionality by deploying the ubuntu2404-rocm environment:
fluxembourg$ oarsub -t exotic -t deploy -p vianden -I
fluxembourg$ kadeploy3 -m vianden-1 ubuntu2404-rocm
More information in the Exotic page.
This cluster was funded by the University of Luxembourg.
[1] https://www.grid5000.fr/w/Luxembourg:Hardware#vianden
-- Grid'5000 Team 11:30, 27 June 2025 (CEST)
![]() Cluster "hydra" is now in the default queue in Lyon
Cluster "hydra" is now in the default queue in Lyon
We are pleased to announce that the hydra[1] cluster of Lyon is now available in the default queue.
As a reminder, Hydra is a cluster composed of 4 NVIDIA Grace-Hopper servers[2].
Each node features:
Due to its bleeding-edge hardware, the usual Grid'5000 environments are not supported by default for this cluster.
(Hydra requires system environments featuring a Linux kernel >= 6.6). The default system on the hydra nodes is based on Debian 11, but **does not provide functional GPUs**. However, users may deploy the ubuntugh2404-arm64-big environment, which is similar to the official Nvidia image provided for this machine and provides GPU support.
To submit a job on this cluster, the following command may be used:
oarsub -t exotic -p hydra
This cluster is funded by INRIA and by Laboratoire de l'Informatique du Parallélisme with ENS Lyon support.
[1] Hydra is the largest of the modern constellations according to Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydra_(constellation)
[2] https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-grace-hopper-superchip-architecture-in-depth/
-- Grid'5000 Team 16:42, 12 June 2025 (CEST)
![]() Cluster "estats" (Jetson nodes in Toulouse) is now kavlan capable
Cluster "estats" (Jetson nodes in Toulouse) is now kavlan capable
The network topology of the estats Jetson nodes can now be configured, just like for other clusters.
More info in the Network reconfiguration tutorial.
-- Grid'5000 Team 18:25, 21 May 2025 (CEST)
Grid'5000 sites
Current funding
INRIA |
CNRS |
UniversitiesIMT Atlantique |
Regional councilsAquitaine |