Grid5000:Home
|
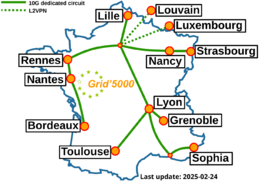
Grid'5000 is a large-scale and flexible testbed for experiment-driven research in all areas of computer science, with a focus on parallel and distributed computing including Cloud, HPC and Big Data and AI. Key features:
Grid'5000 is merging with FIT to build the SILECS Infrastructure for Large-scale Experimental Computer Science. Read an Introduction to SILECS (April 2018)
Older documents:
|
Random pick of publications
Five random publications that benefited from Grid'5000 (at least 2780 overall):
- Louis-Claude Canon, Damien Landré, Laurent Philippe, Jean-Marc Pierson, Paul Renaud-Goud. Assessing Power Needs to Run a Workload with Quality of Service on Green Datacenters. 29th International European Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing (EURO-PAR 2023), Aug 2023, Limassol, Cyprus. pp.229--242, 10.1007/978-3-031-39698-4_16. hal-04257315 view on HAL pdf
- Pierre-Etienne Polet. Portage des chaînes de traitement sonar sur architecture hétérogène : conception et évaluation d'un environnement de programmation basé sur les tâches moldables. Informatique cs. Ecole normale supérieure de lyon - ENS LYON, 2024. Français. NNT : 2024ENSL0004. tel-04633261 view on HAL pdf
- Quentin Guilloteau, Florina M Ciorba, Millian Poquet, Dorian Goepp, Olivier Richard. Longevity of Artifacts in Leading Parallel and Distributed Systems Conferences: a Review of the State of the Practice in 2023. REP 2024 - ACM Conference on Reproducibility and Replicability, ACM, Jun 2024, Rennes, France. pp.1-14, 10.1145/3641525.3663631. hal-04562691 view on HAL pdf
- Thomas Firmin, Pierre Boulet, El-Ghazali Talbi. Parallel Hyperparameter Optimization Of Spiking Neural Networks. 2023. hal-04464394 view on HAL pdf
- Emile Cadorel, Dimitri Saingre. A Protocol to Assess the Accuracy of Process-Level Power Models. Cluster 2024, IEEE, Sep 2024, Kobe, Japan. hal-04720926 view on HAL pdf
Latest news
The first SLICES-FR School is organized from July 7th to 11th in Lyon.
This free event, co-organized with the PEPR Cloud and Networks of the Future, brings together researchers, engineers and professionals to explore advances in distributed computing, edge computing, reprogrammable networks and the IoT.
![]() Cluster "vianden" is now in the default queue in Luxembourg
Cluster "vianden" is now in the default queue in Luxembourg
We are pleased to announce that the vianden[1] cluster of Luxembourg is now available in the default queue.
Vianden is a cluster of a single node with 8 MI300X AMD GPUs.
The node features:
The AMD MI300X GPUs are not supported by Grid'5000 default system (Debian 11). However, one can easily unlock full GPU functionality by deploying the ubuntu2404-rocm environment:
fluxembourg$ oarsub -t exotic -t deploy -p vianden -I
fluxembourg$ kadeploy3 -m vianden-1 ubuntu2404-rocm
More information in the Exotic page.
This cluster was funded by the University of Luxembourg.
[1] https://www.grid5000.fr/w/Luxembourg:Hardware#vianden
-- Grid'5000 Team 11:30, 27 June 2025 (CEST)
![]() Cluster "hydra" is now in the default queue in Lyon
Cluster "hydra" is now in the default queue in Lyon
We are pleased to announce that the hydra[1] cluster of Lyon is now available in the default queue.
As a reminder, Hydra is a cluster composed of 4 NVIDIA Grace-Hopper servers[2].
Each node features:
Due to its bleeding-edge hardware, the usual Grid'5000 environments are not supported by default for this cluster.
(Hydra requires system environments featuring a Linux kernel >= 6.6). The default system on the hydra nodes is based on Debian 11, but **does not provide functional GPUs**. However, users may deploy the ubuntugh2404-arm64-big environment, which is similar to the official Nvidia image provided for this machine and provides GPU support.
To submit a job on this cluster, the following command may be used:
oarsub -t exotic -p hydra
This cluster is funded by INRIA and by Laboratoire de l'Informatique du Parallélisme with ENS Lyon support.
[1] Hydra is the largest of the modern constellations according to Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydra_(constellation)
[2] https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-grace-hopper-superchip-architecture-in-depth/
-- Grid'5000 Team 16:42, 12 June 2025 (CEST)
![]() Cluster "estats" (Jetson nodes in Toulouse) is now kavlan capable
Cluster "estats" (Jetson nodes in Toulouse) is now kavlan capable
The network topology of the estats Jetson nodes can now be configured, just like for other clusters.
More info in the Network reconfiguration tutorial.
-- Grid'5000 Team 18:25, 21 May 2025 (CEST)
Grid'5000 sites
Current funding
As from June 2008, Inria is the main contributor to Grid'5000 funding.
INRIA |
CNRS |
UniversitiesIMT Atlantique |
Regional councilsAquitaine |