Grid5000:Home
|
Grid'5000 is a large-scale and flexible testbed for experiment-driven research in all areas of computer science, with a focus on parallel and distributed computing including Cloud, HPC and Big Data and AI. Key features:
Grid'5000 is merging with FIT to build the SILECS Infrastructure for Large-scale Experimental Computer Science. Read an Introduction to SILECS (April 2018)
Older documents:
|
Random pick of publications
Five random publications that benefited from Grid'5000 (at least 2937 overall):
- Barbara Gendron, Gaël Guibon. SEC : contexte émotionnel phrastique intégré pour la reconnaissance émotionnelle efficiente dans la conversation. 35èmes Journées d'Études sur la Parole (JEP 2024) 31ème Conférence sur le Traitement Automatique des Langues Naturelles (TALN 2024) 26ème Rencontre des Étudiants Chercheurs en Informatique pour le Traitement Automatique des Langues (RECITAL 2024), Jul 2024, Toulouse, France. pp.219-233. hal-04623019 view on HAL pdf
- Wedan Emmanuel Gnibga, Andrew A Chien, Anne Blavette, Anne-Cécile Orgerie. FlexCoolDC: Datacenter Cooling Flexibility for Harmonizing Water, Energy, Carbon, and Cost Trade-offs. e-Energy 2024 - 15th ACM International Conference on Future and Sustainable Energy Systems, Jun 2024, Singapore, Singapore. pp.108-122, 10.1145/3632775.3661936. hal-04581701 view on HAL pdf
- Vincent Alba, Olivier Aumage, Denis Barthou, Raphaël Colin, Marie-Christine Counilh, et al.. Performance portability of generated cardiac simulation kernels through automatic dimensioning and load balancing on heterogeneous nodes. PDSEC 2024, May 2024, San Francisco (CA, USA), United States. 10.1109/IPDPSW63119.2024.00171. hal-04606388v2 view on HAL pdf
- Louis Roussel, François Lemaire. Deep Learning for Integro-Differential Modelling. 2025. hal-05230281 view on HAL pdf
- Jan Aalmoes. Intelligence artificielle pour des services moraux : Concilier équité et confidentialité. Intelligence artificielle cs.AI. INSA de Lyon, 2024. Français. NNT : 2024ISAL0126. tel-05014177 view on HAL pdf
Latest news
![]() Cluster Sasquatch is now in default queue at Grenoble
Cluster Sasquatch is now in default queue at Grenoble
We are pleased to announce that the Sasquatch [1] cluster is now available in the default queue.
Sasquatch is a cluster composed of 2 HPE RL300 nodes, each featuring:
This cluster was funded by the PEPR IA.
[1] https://www.grid5000.fr/w/Grenoble:Hardware#sasquatch
[2] https://amperecomputing.com/briefs/ampere-altra-family-product-brief
Best regards, Grid'5000 Technical Team
-- Grid'5000 Team 10:15, 11 February 2026 (CEST)
![]() Cluster Spirou is now in default queue at Louvain
Cluster Spirou is now in default queue at Louvain
We are pleased to announce that the Spirou[1] cluster of the newly installed Louvain site is now available in the default queue.
Spirou is a cluster composed of 8 Lenovo ThinkSystem SR630 V2 nodes, each featuring:
Be aware that we noticed I/Os inconsistencies on this cluster.
We advise users to take this into account when performing experimentations on the cluster. See the following bug for more information: https://intranet.grid5000.fr/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=16938
This cluster was funded by the Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique – FNRS (F.R.S.–FNRS), and its operation is supported by F.R.S.–FNRS and the Wallonia region (SPW).
[1] https://www.grid5000.fr/w/Louvain:Hardware#spirou
Best regards,
Grid'5000 Technical Team
-- Grid'5000 Team 10:24, 12 January 2026 (CEST)
![]() End of support for centOS7/8 and centOSStream8 environments
End of support for centOS7/8 and centOSStream8 environments
Support for the centOS7/8 and centOSStream8 kadeploy environments is stopped due to the end of upstream support and compatibility issues with recent hardware.
The last version of the centOS7 environments (version 2024071117), centOS8 environments (version 2024071119), centOSStream8 environments (version 2024070316) will remain available on /grid5000. Older versions can still be accessed in the archive directory (see /grid5000/README.unmaintained-envs for more information).
-- Grid'5000 Team 08:44, 4 December 2025 (CEST)
![]() Ecotaxe cluster is now in default queue at Nantes
Ecotaxe cluster is now in default queue at Nantes
We are pleased to announce that the ecotaxe cluster of Nantes is now available in the default queue.
As a reminder, ecotaxe is a cluster composed of 2 HPE ProLiant DL385 Gen10 Plus v2 servers[1].
Each node features:
To submit a job on this cluster, the following command may be used:
oarsub -t exotic -p ecotaxe
This cluster is co-funded by Région Pays de la Loire, FEDER and REACT EU via the CPER SAMURAI [3].
[1] https://www.grid5000.fr/w/Nantes:Hardware#ecotaxe
[2] The observed throughput depends on multiple parameters such as the workload, the number of streams, ... [3] https://www.imt-atlantique.fr/fr/recherche-innovation/collaborer/projet/samurai
-- Grid'5000 Team 14:10, 02 December 2025 (CET)
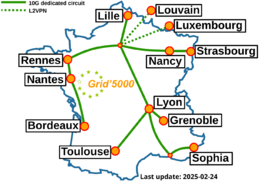
Grid'5000 sites
Current funding
As from June 2008, Inria is the main contributor to Grid'5000 funding.
INRIA |
CNRS |
UniversitiesIMT Atlantique |
Regional councilsAquitaine |