Grid5000:Network: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Grid5000 project== | ==Grid5000 project== | ||
[[Image:renater5-g5k.jpg|250px|right|thumbnail|10Gbps lambda activated for Grid'5000 in Renater's Dark Fiber infrastructure]] | [[Image:renater5-g5k.jpg|250px|right|thumbnail|10Gbps lambda activated for Grid'5000 in Renater's Dark Fiber infrastructure]] | ||
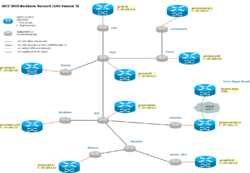
[[Image:Schema_Backbone.png|250px|right|thumbnail|Grid5000 IP Network]] | |||
===Initial design=== | ===Initial design=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
* [http://www.naregi.org NAREGI], more information is available on [[Naregi-Grid5000]] | * [http://www.naregi.org NAREGI], more information is available on [[Naregi-Grid5000]] | ||
= Grid'5000 Sites | = Grid'5000 Sites = | ||
Each local network topology is different. More information is available to our users on the following pages of the Wiki : | |||
* [[Bordeaux:Network|Bordeaux]] | |||
* [[Grenoble:Network|Grenoble]] | |||
* [[Lille:Network|Lille]] | |||
* [[Lyon:Network|Lyon]] | |||
* [[Nancy:Network|Nancy]] | |||
* [[Orsay:Network|Orsay]] | |||
* [[Rennes:Network|Rennes]] | |||
* [[Sophia:Network|Sophia-Antipolis]] | |||
* [[Toulouse:Network|Toulouse]] | |||
== High Speed Networks | == High Speed Networks== | ||
Grid'5000 features both Myrinet and Infiniband network infrastructures ([[Special:G5KHardware#High_performance_network_families|See high speed networks availability]]). | Grid'5000 features both Myrinet and Infiniband network infrastructures ([[Special:G5KHardware#High_performance_network_families|See high speed networks availability]]). | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 9 June 2009
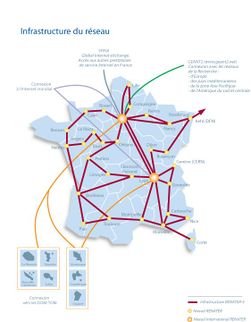
Grid'5000 backbone network infrastructure
Grid'5000 backbone network infrastructure is provided by RENATER
RENATER is the French National Telecommunication Network for Technology, Education and Research. More information can be found on the web site: http://www.renater.fr
RENATER offers about 30 POPs (Points Of Presence) in France, at least one POP for each region, which metropolitan and regional networks are connected on.
More than 600 sites (Universities, Research Centers, ..) are interconnected through RENATER.
The actual phase of the network is RENATER-5, the deployment has been completed by January 2009.
The "standard" architecture is based on 10Gbit/s dark fibers and provides IP transit connectivity, interconnection with GEANT-2 (http://www.geant2.net/), overseas territories and the SFINX (Global Internet exchange).
For more information on the Grid5000 Backbone Network Architecture, please check the Network_interlink page.
Grid5000 project
Initial design
The initial design of Grid'5000 sites interconnection has been adressed within the RENATER backbone using a Ethernet Over MPLS (EoMPLS) solution. It used to be full mesh topology based on MPLS tunnels (LSPs) established between the RENATER PoPs on which are connected the Grid'5000 sites. Sites were interconnected through 1Gbit/s VLANs.
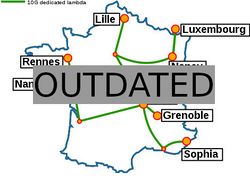
Dark fibre
RENATER-4 introduced a dark fibre infrastructure allowing to allocate dedicated 10Gbit/s "lambdas" for specific research projects. It also provides interconnection with GEANT-2 (see picture above), with increased capacity compared to GEANT-1 and dedicated interconnection for projects. RENATER-5 has enhanced the dark fiber infrastructure and all Grid'5000 sites are now connected to it.
Grid'5000 sites see each others inside the same VLAN at 10Gbit/s speed (while a few bottleneck still exists, like the Lyon to Paris fiber).
Monitoring and Metrology
You can find the monitoring and metrology done on Grid5000 by Renater and the Grid5000 staff on the Network_interlink#Monitoring section.
International Extensions
We share a direct connection with the following networks :
- DAS-3, more information is available on DAS3-Grid5000
- NAREGI, more information is available on Naregi-Grid5000
Grid'5000 Sites
Each local network topology is different. More information is available to our users on the following pages of the Wiki :
High Speed Networks
Grid'5000 features both Myrinet and Infiniband network infrastructures (See high speed networks availability).