Getting Started: Difference between revisions
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
== Visualization and reservation of Grid'5000 resources == | == Visualization and reservation of Grid'5000 resources == | ||
{{Todo|text= | |||
infos sur les sites: MOTD, pages sites du Wiki | |||
page Status (gantt, monika, etc.) | |||
reservation of resources (oarsub) | |||
run oarsub -I -> you are now connected to a node, reserved for your usage for an hour | |||
exit -> you are now disconnected | |||
oarsub 'sleep 3600' , oarsub -C <jobid> | |||
visualize resources: MOTD, Gantt, Monika, API selector | |||
complex oarsub (-p cluster, -l nodes/walltime, -r) | |||
list resources, connect to them using oarsh, or use -t classic-ssh if you want to keep to pure ssh (pointeur vers advanced) | |||
your software environment on nodes is the production environment, you can use for MPI, JAVA applications or to start VMs using KVM. You might want more control (to be root)}} | |||
== Get root access and create your own experimental environment with Kadeploy == | |||
{{Todo|text=oarsub -t deploy | |||
kadeploy3 | |||
installer un paquet | |||
http_proxy (whitelisting) | |||
save for furture usage or script installation | |||
Kaconsole et Kareboot ou kapower3 | |||
parler de g5k-checks, du focus XP de G5K, expliquer que g5k-checks compare ses données avec l'API de réference, et donc introduire l'API}} | |||
== Conclusion == | |||
{{Todo|text=summarize important stuff seen in this tutorial}} | |||
{{Todo|text=introduce next tutorials}} | |||
== (TODO list) Firsts steps == | == (TODO list) Firsts steps == | ||
# G5K general goals and admin context + orga + get support | # G5K general goals and admin context + orga + get support | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 25 October 2012
Grid'5000 is a scientific instrument (a testbed) that supports large-scale, reproducible experiments in the context of research on distributed systems (Cloud, Grid, HPC, P2P systems).
This tutorial will guide you through your first steps on Grid'5000. Before proceeding, make sure you have a Grid'5000 account (if not, follow this procedure), and an SSH client.
Getting support
The Support page describes how to get help during your Grid'5000 usage.
Connecting for the first time and preparing your SSH environment
Step 1: Connect to Grid'5000
You will get authenticated using the SSH public key you provided in the account creation form.
The access.grid5000.fr address points to two actual machines: access-south in Sophia and access-north in Lille. Those machines provide SSH access to Grid'5000 from Internet.
| Note | |
|---|---|
If you prefer, you might also be able to connect directly to your local Grid'5000 site, but per-site access restrictions are applied, so using | |
Grid'5000 is structured in sites (Grenoble, Rennes, Nancy, ...). Each site hosts one or more clusters.
The primary way to move around Grid'5000 is using SSH. It is recommended that you use a second SSH key, created without a passphrase, and that you use it inside Grid'5000 to move around. The next steps of this tutorial will guide you through creating that SSH key, and configuring your SSH environment on all sites.
Step 2: Create an new SSH key with ssh-keygen
You have a different home directory on each Grid'5000 site, so you will usually use Rsync or scp to move data around. Note that home directories on Grid'5000 are not backed up: it is your responsibility to save important data outside Grid'5000 (or to copy data to several Grid'5000 sites in order to increase redundancy).
Also note that quotas are applied -- by default, you get about 25 GB per Grid'5000 site. If your usage of Grid'5000 requires more disk space, it is possible to request quota extensions in the account management interface, or to use other storage solutions (see Storage5k).
| Todo | |
|---|---|
update reference to Storage5k tutorial once it is written. the current page does not look like a user-friendly tutorial | |
On access machines, you have direct access to each of those home directory (through NFS mounts). In the next two steps of this tutorial, we will use that feature to propagate your SSH key to each site. First, we will prepare your SSH configuration for one site, then we will copy it to all other sites.
Step 3: Prepare your SSH configuration on one site
We will prepare the bordeaux site, then duplicate its configuration everywhere.
First, copy your new SSH keys to your .ssh directory in bordeaux:
Now, add your new SSH public key to bordeaux's authorized_keys file:
Step 4: Push your SSH configuration to all sites
We will use a shell trick to copy your SSH configuration to all sites, and to the other access machine:
An error message about bordeaux is normal.
Step 5: Use SSH to connect to another site
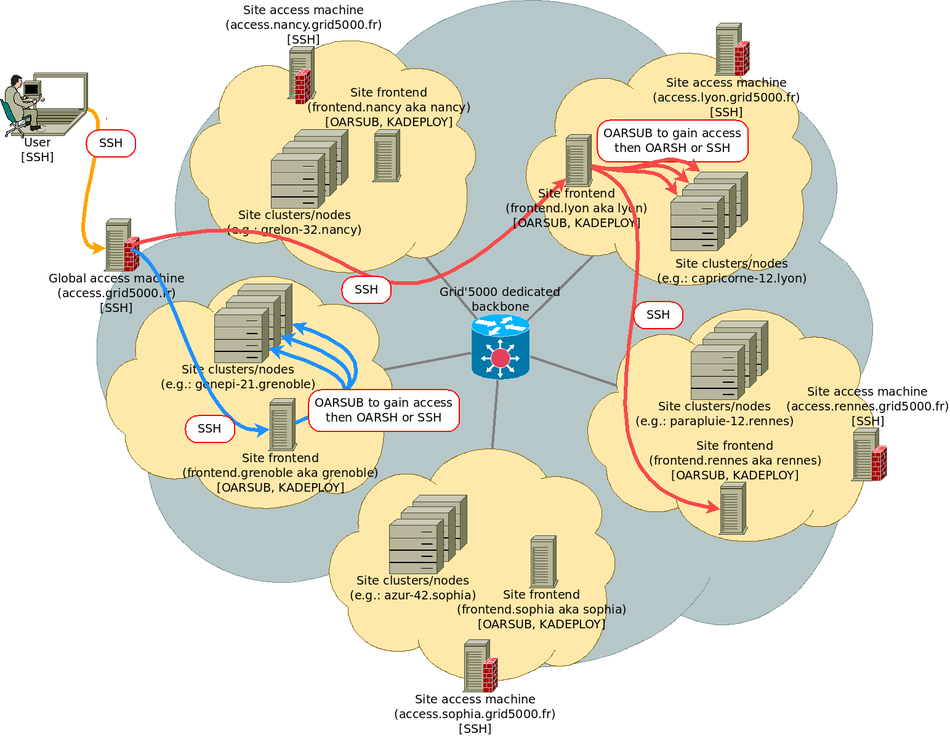
The figure below shows how you just connected from your local machine to access, and then to the site frontend in nancy. Site frontends (named fsite.site.grid5000.fr or simply site.grid5000.fr) are the machines you will use to interact with Grid'5000 tools such as OAR and Kadeploy. Those machines are virtual machines, and must not be used for CPU or I/O intensive tasks (nodes must be used instead).
| Note | |
|---|---|
If you are using Linux, Mac OS X, or another Unix-based system, it is recommended to configure your SSH client to enable shortcuts. Once done, you will be able to connect to any machine inside Grid'5000 in one shot, using | |
Visualization and reservation of Grid'5000 resources
Get root access and create your own experimental environment with Kadeploy
Conclusion
(TODO list) Firsts steps
- G5K general goals and admin context + orga + get support
- ssh access.grid5000.fr
- you are now connected to Grid'5000 from here you can
- see the contents of your homedir on each site (these are different, and not backed-up)
- connect to a site
- you are now connected to Grid'5000 from here you can
- ssh-keygen + installer les clés sur les sites. See the FAQ on how to allow direct access from your machine to a site.
- connect to a site
- run oarsub -I -> you are now connected to a node, reserved for your usage for an hour
- exit -> you are now disconnected
- oarsub 'sleep 3600' , oarsub -C <jobid>
- visualize resources: MOTD, Gantt, Monika, API selector
- complex oarsub (-p cluster, -l nodes/walltime, -r)
- list resources, connect to them using oarsh, or use -t classic-ssh if you want to keep to pure ssh (pointeur vers advanced)
- your software environment on nodes is the production environment, you can use for MPI, JAVA applications or to start VMs using KVM. You might want more control (to be root)
- oarsub -t deploy
- kadeploy3
- installer un paquet
- http_proxy (whitelisting)
- save for furture usage or script installation
- Kaconsole et Kareboot ou kapower3
- parler de g5k-checks, du focus XP de G5K, expliquer que g5k-checks compare ses données avec l'API de réference, et donc introduire l'API