Grid5000:Home: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=== Grid'5000 users get 2 out of 3 [http://www.ipdps.org/ipdps2011/2011_phd_forum.html Best Poster award at IPDPS 2011] === | === Grid'5000 users get 2 out of 3 [http://www.ipdps.org/ipdps2011/2011_phd_forum.html Best Poster award at IPDPS 2011] === | ||
Congratulations go to Alexandra Carpen-Amarie ( IRISA, University Rennes 1, INRIA, Rennes, France) for her poster ''Towards a Self-Adaptive Data Management System for Cloud Environments'' and to Pierre Riteau (INRIA, IRISA, Rennes, France) for his poster ''Building Large Scale Dynamic Computing Infrastructures over Distributed Clouds'' | Congratulations go to Alexandra Carpen-Amarie ( IRISA, University Rennes 1, INRIA, Rennes, France) for her poster ''Towards a Self-Adaptive Data Management System for Cloud Environments'' and to Pierre Riteau (INRIA, IRISA, Rennes, France) for his poster ''Building Large Scale Dynamic Computing Infrastructures over Distributed Clouds'' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Grid5000:News|read more news]] | [[Grid5000:News|read more news]] | ||
Revision as of 09:00, 21 June 2011
|
|
Latest updates from Grid'5000 users
- Experiments
{{#experiments:3|||**}}
- Publications
Five random publications that benefited from Grid'5000 (at least 2937 overall):
- Sweta Suresh, Maxime Guillaud. Belief Propagation Decoding of Tensor-Based Modulation for Unsourced Random Access. IZS 2026 - International Zurich Seminar on Information and Communication, Feb 2026, Zurich, Switzerland. hal-05451488 view on HAL pdf
- Léo Valque. 3D Snap rounding. Computer Science cs. Université de Lorraine, 2024. English. NNT : 2024LORR0337. tel-05016163 view on HAL pdf
- Daniel Richards Arputharaj, Charlotte Rodriguez, Angelo Rodio, Giovanni Neglia. Green Federated Learning via Carbon-Aware Client and Time Slot Scheduling. MASCOTS 2025 - 33rd International Symposium on the Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication System, Oct 2025, Paris, France. 10.1109/MASCOTS67699.2025.11283314. hal-05423023 view on HAL pdf
- Ali Golmakani, Mostafa Sadeghi, Xavier Alameda-Pineda, Romain Serizel. A weighted-variance variational autoencoder model for speech enhancement. ICASSP 2024 - International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE, Apr 2024, Seoul (Korea), South Korea. pp.1-5, 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10446294. hal-03833827v2 view on HAL pdf
- Sayf Halmi, Aurora Rossi, Frédéric Giroire, Nicolas Nisse, Michele Pezzoni. La vie risquée mais enrichissante d'un doctorant interdisciplinaire : accrochez-vous, une seule publication suffit !. Universite Cote d'Azur. 2026. hal-05518683 view on HAL pdf
Latest news
First Cheat sheet created
If you are of those who enjoy a recap of the different commands and links to the main help pages, you'll be pleased to see that an admin has contributed the first Grid'5000 cheat sheet to this wiki. If you wish to understand how it was built, you can read and suggest contributions in the corresponding bug.
Grid'5000 users get 2 out of 3 Best Poster award at IPDPS 2011
Congratulations go to Alexandra Carpen-Amarie ( IRISA, University Rennes 1, INRIA, Rennes, France) for her poster Towards a Self-Adaptive Data Management System for Cloud Environments and to Pierre Riteau (INRIA, IRISA, Rennes, France) for his poster Building Large Scale Dynamic Computing Infrastructures over Distributed Clouds
Grid'5000 at a glance
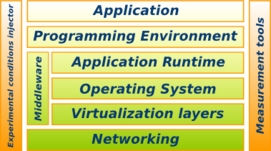
- Grid'5000 is a scientific instrument for the study of large scale parallel and distributed systems. It aims at providing a highly reconfigurable, controlable and monitorable experimental platform to its users. The initial aim (circa 2003) was to reach 5000 processors in the platform. It has been reframed at 5000 cores, and was reached during winter 2008-2009.
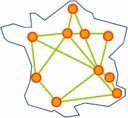
- The infrastructure of Grid'5000 is geographically distributed on different sites hosting the instrument, initially 9 sites in France (10 since 2011). Porto Alegre, Brazil is now officially becoming the first site abroad.
Sites:
- Grid'5000 is a research effort developing a large scale nation wide infrastructure for large scale parallel and distributed computing research.
- 19 laboratories are involved in France with the objective of providing the community a testbed allowing experiments in all the software layers between the network protocols up to the applications.
The current plans are to extend from the 9 initial sites each with 100 to a thousand PCs, connected by the RENATER Education and Research Network to a bigger platform including a few sites outside France not necessarily connected through a dedicated network connection. Sites in Brazil and Luxembourg should join shortly, and Reims has now joined.
All sites in France are connected to RENATER with a 10Gb/s link, except Reims, for the time linked through a 1Gb/s
This high collaborative research effort is funded by INRIA, CNRS, the Universities of all sites and some regional councils.
ALADDIN-G5K : ensuring the development of Grid'5000
For the 2008-2012 period, Engineers ensuring the development and day to day support of the infrastructure are mostly provided by INRIA, under the ADT ALADDIN-G5K initiative.
HEMERA: Demonstrating ambitious up-scaling techniques on Grid'5000
Héméra is an INRIA Large Wingspan project, started in 2010, that aims at demonstrating ambitious up-scaling techniques for large scale distributed computing by carrying out several dimensioning experiments on the Grid’5000 infrastructure, at animating the scientific community around Grid’5000 and at enlarging the Grid’5000 community by helping newcomers to make use of Grid’5000.
Initial Rationale
The foundations of Grid'5000 have emerged from a thorough analysis and numerous discussions about methodologies used for scientific research in the Grid domain. A report presents the rationale for Grid'5000.
In addition to theory, simulators and emulators, there is a strong need for large scale testbeds where real life experimental conditions hold. The size of Grid'5000, in terms of number of sites and number of processors per site, was established according to the scale of the experiments and the number of researchers involved in the project.
Current funding
As from June 2008, INRIA is the main contributor to Grid'5000 funding.
INRIA |
CNRS |
UniversitiesUniversity Joseph Fourier, Grenoble |
Regional councilsAquitaine |