KaVLAN: Difference between revisions
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
== How to reserve a VLAN == | == How to reserve a VLAN == | ||
KaVLAN only works with ''deploy'' reservations; to obtain nodes and a VLAN, you must reserve | KaVLAN only works with ''deploy'' reservations; to obtain nodes and a VLAN, you must reserve kavlan resources (VLAN-IDs) with the <code class="command">oarsub</code> command. There are 3 kinds of resources defined in OAR: '''kavlan''', '''kavlan-local''', '''kavlan-global'''. For example, if you need 3 nodes and a local VLAN, you can run: | ||
{{Term|location=frontend|cmd=<code class="command">oarsub</code> -t deploy -l {"type='kavlan-local'"}/vlan=1+/nodes=3 -I}} | {{Term|location=frontend|cmd=<code class="command">oarsub</code> -t deploy -l {"type='kavlan-local'"}/vlan=1+/nodes=3 -I}} | ||
Revision as of 14:56, 14 January 2016
Overview
The goal of Kavlan is to allow people to manage VLAN on Grid'5000 nodes. The benefit is a complete level 2 isolation. It can be used together with OAR and Kadeploy to do some experimentations.
Installation status for all sites:
| Sites | Version | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Grenoble | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Lille | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Luxembourg | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Lyon | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Nancy | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Nantes | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Rennes | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Sophia | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Toulouse | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Strasbourg | 1.2.7-1 | |
| Louvain | 1.2.7-1 |
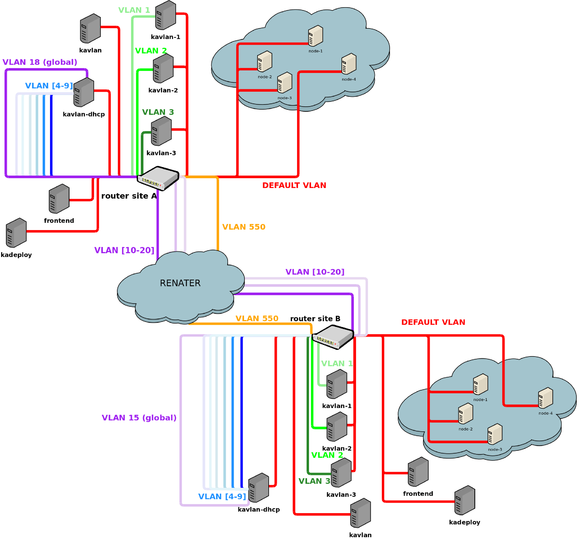
3 types of VLANs are available on Grid'5000:
- local VLANs (in green)
- routed VLANs (in blue)
- global VLANs (in purple)
1: Isolated VLAN
An isolated VLAN (also called local VLAN) is completely isolated from the rest of Grid'5000: no routing is configured. Therefore, you have to use a special host to reach your nodes inside this kind of VLAN. In that kind of VLAN, a DHCP server is brought up for you, so once you have put your nodes in it, you have to restart the networking service (with kaconsole3, or an 'at' command for instance), or reboot the node (with kareboot3). Then you will be able to reach any of your nodes within the VLAN using hostnames such as hostname-kavlan-VLAN_ID (adding the suffix -kavlan-VLAN_ID to the regular hostname), via the VLAN gateway: kavlan-VLAN-ID.
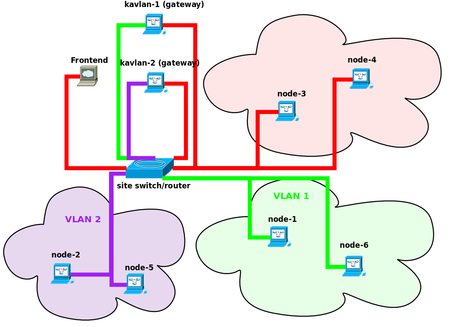
The figure below shows two jobs running with KaVLAN: each job has it's nodes isolated in a local VLAN (purple and green). The other nodes are all in the default VLAN (red). The only way to reach the isolated nodes is to use a gateway node (kavlan-1 and kavlan-2 in the figure). The gateway has two Ethernet interfaces: one in the default VLAN and one in the dedicated VLAN. This way, you can use ssh to reach your nodes. An other way to reach an isolated node is to use the kaconsole command.
2: Routed VLAN
This kind of VLAN is not isolated at the layer 3. Therefore you can reach the nodes inside the VLAN from the rest of Grid5000. No need for an ssh gateway.
Nodes in the vlan are accessible with the hostname : hostname-kavlan-VLAN_ID (like in local vlan, but from the frontend for example)
3: Global VLAN
A global VLAN is a VLAN which is spread on all grid5000 sites (using IEEE 802.1ad encapsulation, also known as QinQ). Therefore you can configure nodes of different sites on the same VLAN (same layer 2 network) ! There will be no routing between these nodes. To reach nodes inside a VLAN, routing is configured on the router of the site where you reserved this global VLAN.
Usage
How to reserve a VLAN
KaVLAN only works with deploy reservations; to obtain nodes and a VLAN, you must reserve kavlan resources (VLAN-IDs) with the oarsub command. There are 3 kinds of resources defined in OAR: kavlan, kavlan-local, kavlan-global. For example, if you need 3 nodes and a local VLAN, you can run:
Then you can get the id of your VLAN using the kavlan command
If you run this command outside the shell started by OAR for your reservation, you must add the oar JOBID.
You should get an integer in the <1-3> range for local VLAN ( the range for routed vlan is <4-9>, and there is one global VLAN per OAR server).
You can get all the options of the command using --help:
# kavlan --help
Usage: kavlan [options]
Specific options:
-i, --vlan-id N set VLAN ID (integer or DEFAULT)
-C, --ca-cert CA CA certificate
-c, --client-cert CERT client certificate
-k, --client-key KEY client key
-l, --get-nodelist Show nodenames in the given vlan
-e, --enable-dhcp Start DHCP server
-d, --disable-dhcp Stop DHCP server
-V, --show-vlan-id Show vlan id of job (needs -j JOBID)
-g, --get-vlan Show vlan of nodes
-s, --set-vlan Set vlan of nodes
-j, --oar-jobid JOBID OAR job id
-m, --machine NODE set nodename (several -m are OK)
-f, --filename NODEFILE read nodes from a file
-u, --user USERNAME username
-v, --[no-]verbose Run verbosely
-q, --[no-]quiet Run quietly
--[no-]debug Run with debug output
-h, --help Show this message
--version Show version
Once you have a kavlan reservation running, you can put your nodes in your VLAN (and back into the default VLAN) at anytime during the lifetime of your job; for local VLAN, you are also allowed to connect to the VLAN gateway named kavlan-<ID> where ID is your vlan ID,
To know how to use your local vlan you can read this tutorial : Network_isolation_on_Grid'5000#Change_the_VLAN_of_your_nodes_manually
If you want to learn how to use KaVLAN, you can try the tutorial on Network isolation on Grid'5000